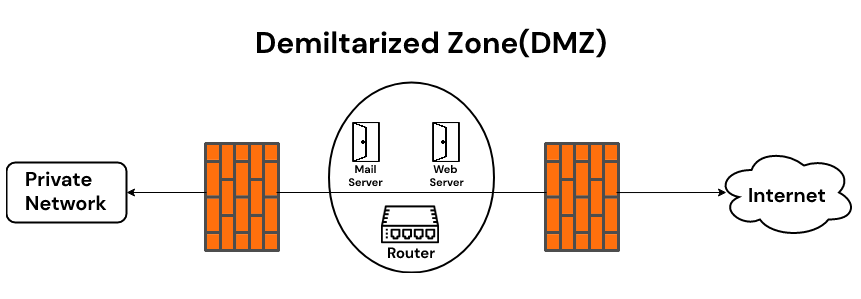
The second portion of my ADCS lab will contain an Active Directory domain in a private network, behind firewalls and routers that also serve a “DMZ” for publicly available services. The idea here is that the domain will be used to administer the services in the DMZ using ADCS to regulate which users can do specific tasks. To establish this there will be two firewalls in place, the first being theDMZ external firewall which handles NAT and port forwarding to the services inside the DMZ using one IP Address to handle connections. This firewall will also later provide the IPSec Site-To-Site VPN from which external networks can be bridged for internal network access as well as administering DMZ services. The second firewall handles connections to the local Active Directory domain.
Building the network in Proxmox
This portion of the lab will be using Proxmox as the virtualization platform on an Intel NUC. Installing Proxmox is beyond the scope of this article, but for our scenario we need to ensure there is one “bridged” network interface to serve as the internet connection for our routers. Beyond this we will need two other network interfaces, one for each routers’ LAN interface two which DMZ and internal network hosts can connect to. This can be done by selecting the root cluster (in my lab there is only one proxmox “node”), navigating to “Network” and creating a new Linux bridge. The bridged interface for internet connections is set up automatically, and no ip addressing information need be supplied for the interfaces as we will be managing this via PFSense. Specifically for this lab they are :
- vmbr0 – bridged connection to the internet, WAN network for DMZ external router
- dmzlan0 – interface for LAN side of DMZ external router, serving DMZ hosts and acting as the WAN network for the internal DMZ router.
- dmzintlan0 – interface for LAN of internal DMZ router, this is where the domain machines will be connected
Creating Virtual Machines in Proxmox
The process of creating virtual machines in proxmox is very similar to doing so in Virtualbox or VmWare, first you must upload the iso file to the directory where iso files are stored. This can be done through the WebUi or via the commandline:
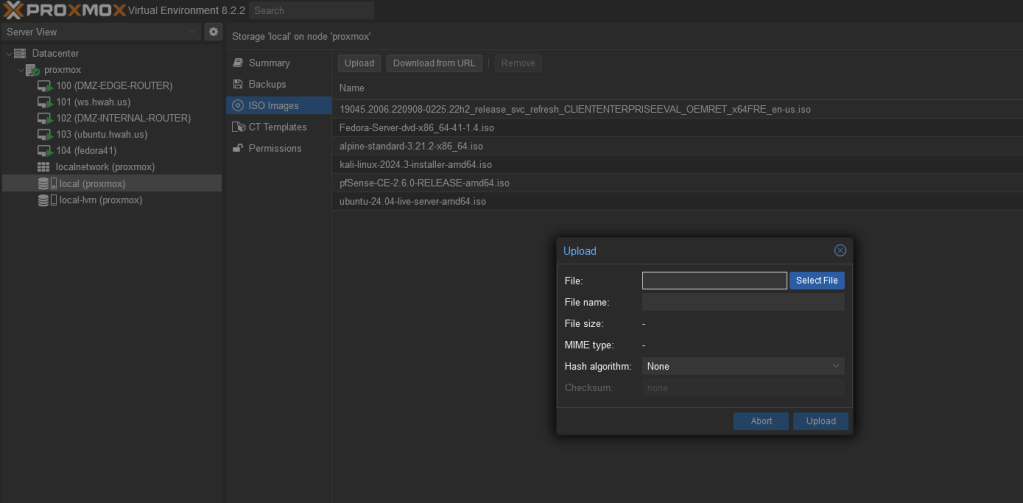
The iso files were stored in /var/lib/vz/template/iso/ on my system so an iso file can be directly downloaded from a site using wget or curl to this directory.
By clicking the “Create VM” button at the top of the web ui, we can start creating Virtual Machines, allocating resources as we see fit.
For the time being I created five virtual machines, leaving the ADCS portion of the lab to do at a later time. The most important being the two firewalls. I set these up just as I did in the previous posts, with the network interfaces as needed.
- DMZ Edge Router with WAN set to DHCP on the bridged interface (vmbr0)
- DMZ Edge Router with LAN set to the dmzlan0 interface given the static ip of 10.10.0.1/24.
- DMZ Internal Router with WAN set to the dmzlan0 interface as well, with a static IP of 10.10.0.254/0
- DMZ Internal Router with LAN set to the dmzintlan0 interface given an internal ip of 172.21.0.1/24
The other three machines are linux servers whose isos I had on disk from previous labs, these will be used to test ADCS integration with DMZ services and Active Directory integration with Linux. I installed the following:
- Alpine Linux as the webserver in the DMZ, with the sole network interface as dmzlan0
- Ubuntu and Fedora servers in the DMZ internal LAN, using network interfaces dmzintlan0
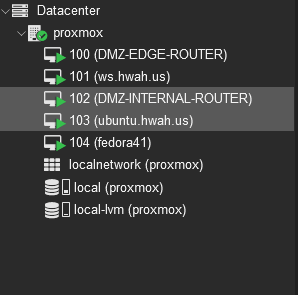
When all was said and done, my cluster looked like this:
Note: with this configuration I did not have a host to configure the PFSense routers with a web browser (traffic to the WebConfiguratior is blocked from WAN access by default). A work around is to use SSH port forwarding on the routers to export the WebConfigurator ports to your local machine. This requires an SSH server to be installed on your machine, with simple instructions on how to do this in Windows found here. Then on the command line for each router you can forward ports in the following way:
ssh -R 8888:localhost:443 user@sshserver.ip
Replacing the the username and ip address to reflect our actual values, this will forward port 443 form the pfsense boxes to port 8888 on the host where the ssh server was installed, allowing us to view the WebConfigurator from a web browser by inputting https://localhost:8888
Wrapping up
At this point we have our second environment ready to go, in subsequent posts I will detail the ADCS installation in this environment as well as creating the IP Sec Site-To-Site VPN to connect the internal DMZ LAN to the network containing the SIEM.
